

DISEASESCoconutRoot (Wilt) Disease
|
 Root (Wilt) Disease affected Palm 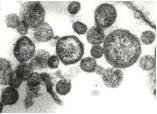 Phytoplasma in sieve tubes of root (wilt) Disease affected Palms Vectors   Lace Bug ----Plant Hopper (Stephanitis typica) --(Proutista moesta) |
Leaf rot disease
|
 Leaf rot Disease affected Palm   Symptoms of leaf rot Disease |
Bud rot
|
 Bud rot affected Palm Bud rot affected Palm  Mancozeb Sachets Mancozeb Sachets |
Stem bleeding
|
 Bleeding Symptoms on the Stem |
Fruit Rot and Immature Nut Fall
|
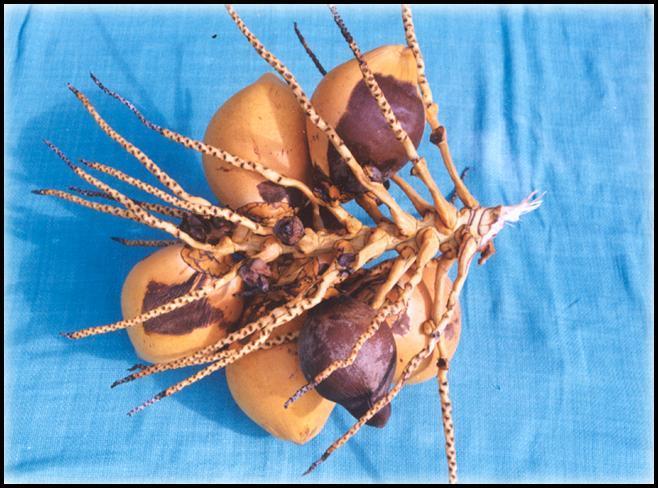 Disease incidence in COD Variety 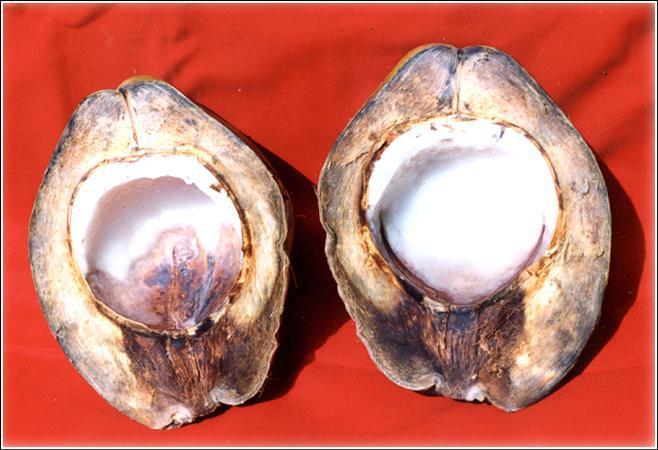 L. theobromae infection spreading to the kernel and causing extensive rotting |
| Arecanut Yellow leaf disease
|
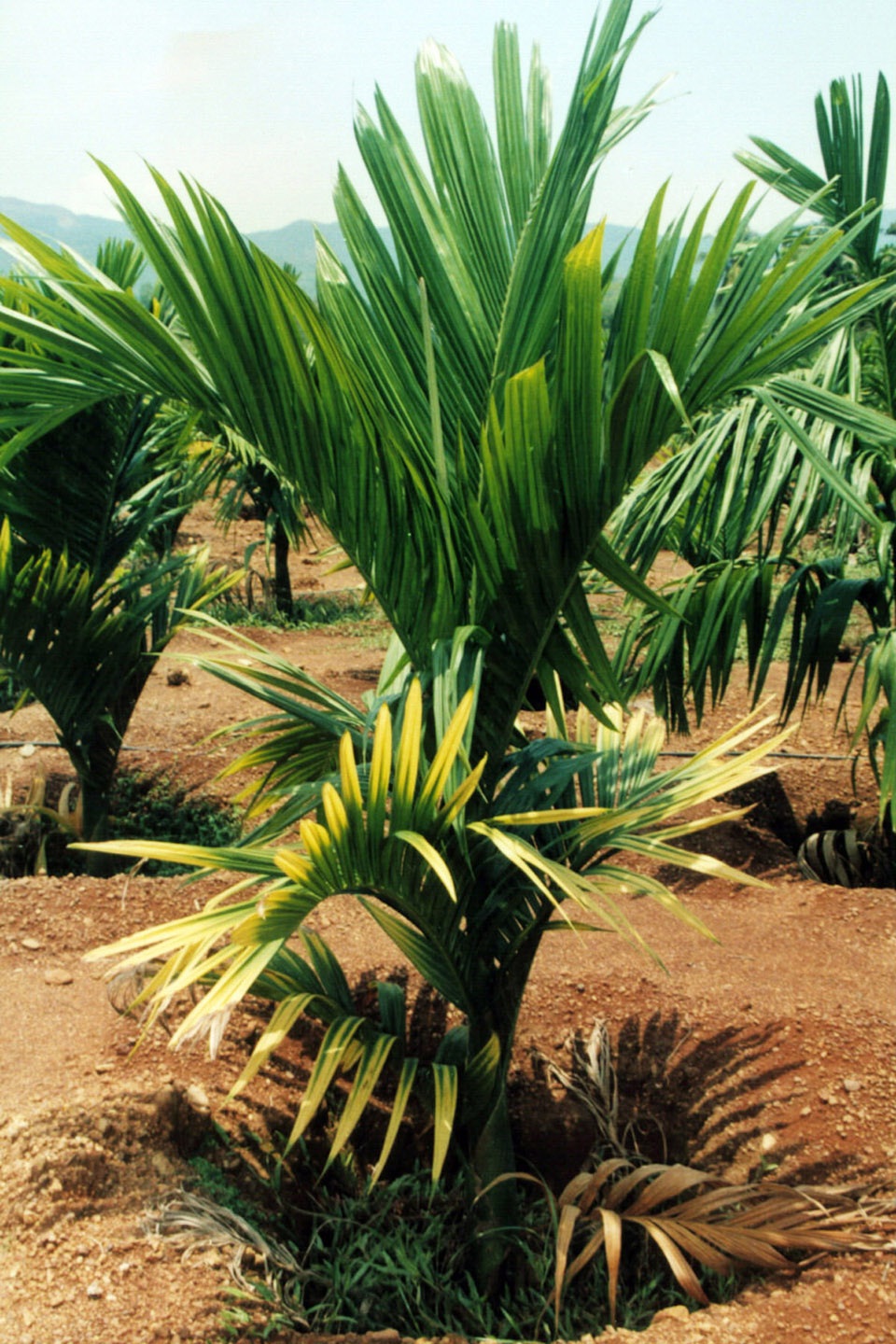 Foliar Symptoms of YLD |
Phytophthora diseases
|
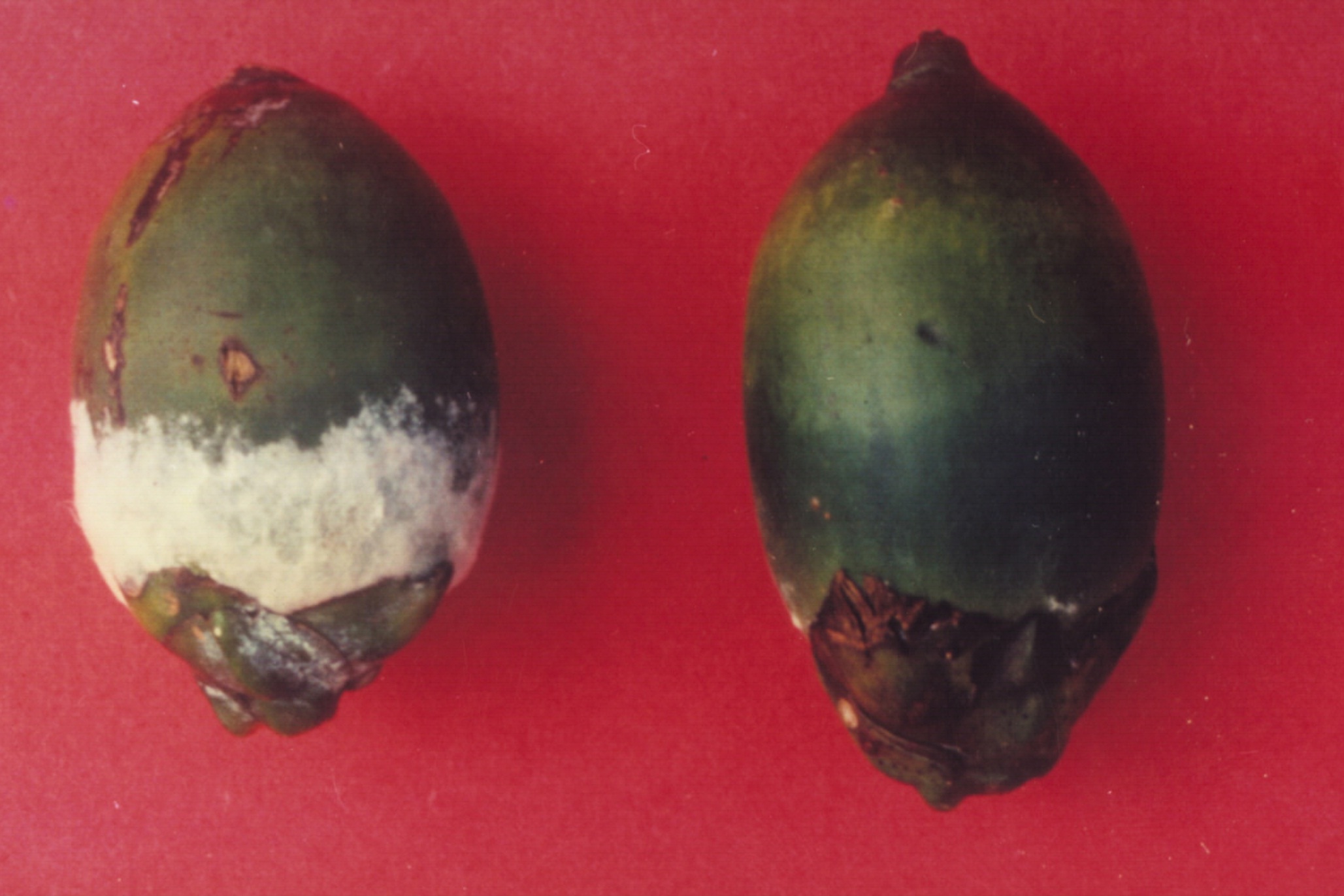 Fruit Rot caused by P.meadii  Bud rot Disease |
Inflorescence dieback and Button shedding
|
 Inflorescence Dieback |
Anabe or Foot Rot
|
 Anabe or Foot Rot |
Cocoa Phytophthora diseases
|
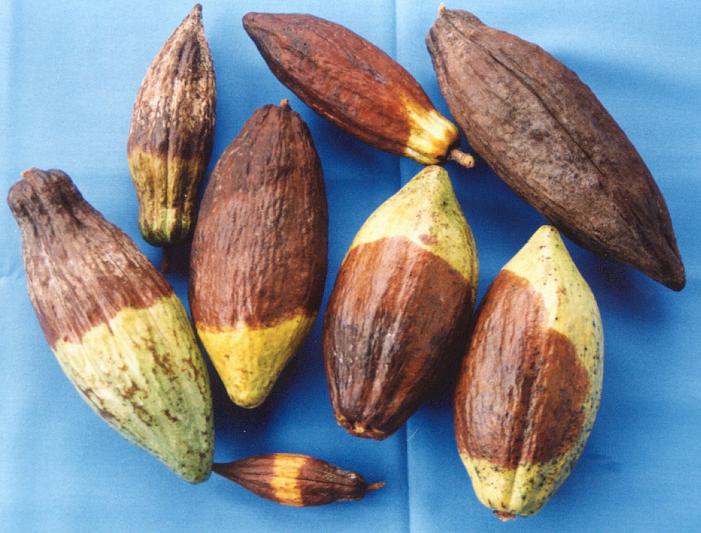 Black Pod Disease caused by P.palmivora  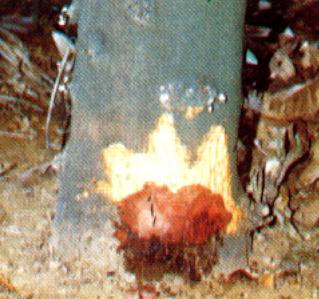 External Lesion -----Internal Lesion Stem Canker |
Cherelle rot
|
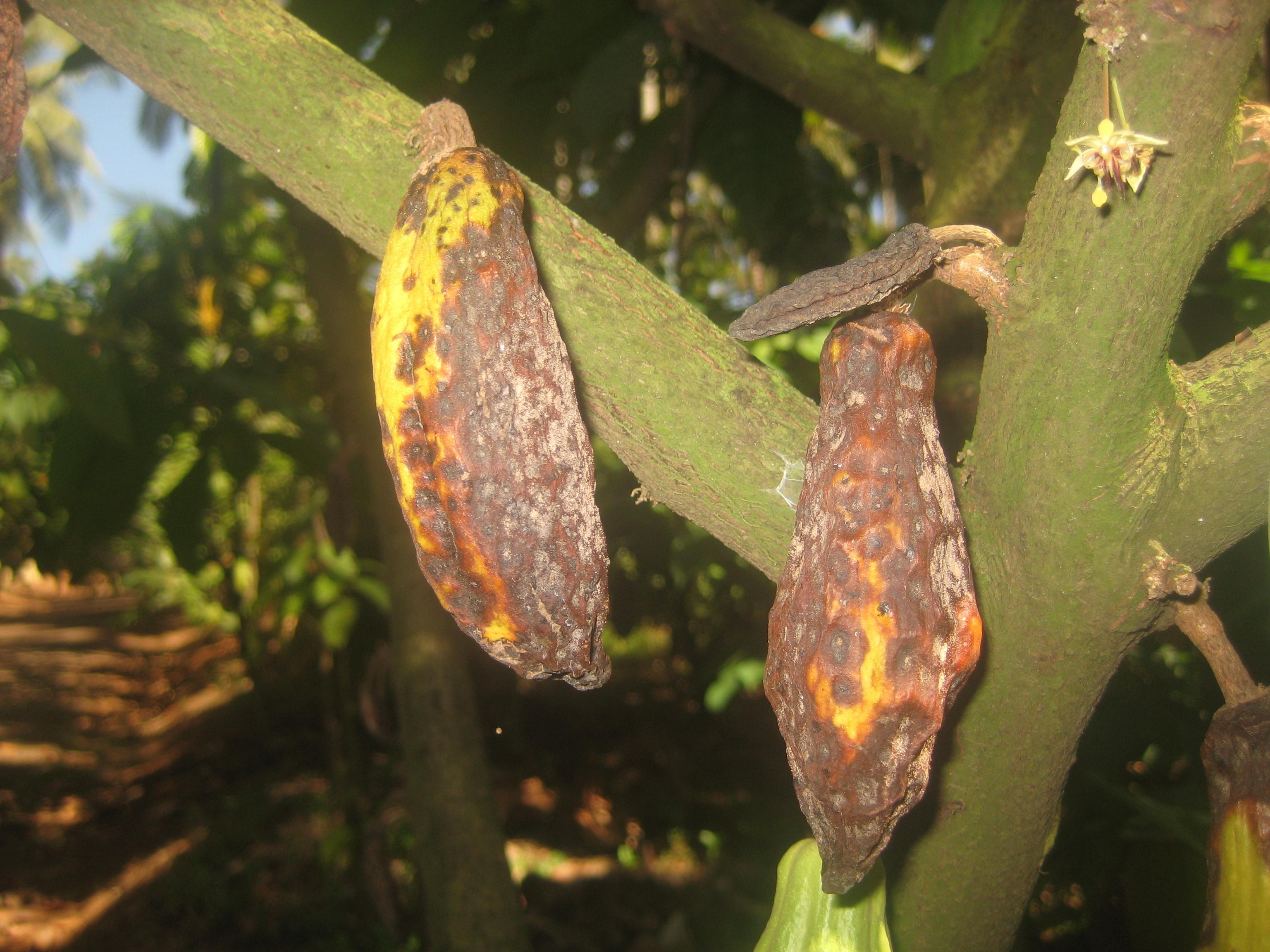 Cherelle rot |
| Utilization of Plantation crop Wastes | |
| Developed low cost techniques for mass multiplication of bio-control agents utilizing plantation crop wastes like coconut water and cocoa sweating. Diluted cocoa sweating was found to be superior to conventional liquid media |  T. harzianum multiplied in Cocoa Sweating T. harzianum multiplied in Cocoa Sweating |
| Developed a simple and highly economical low cost technology for farm level mass production of biocontrol agents using diluted cocoa sweating, bean shell and pod husk |  T. harzianum multiplied in unsterilized Cocoa bean shell moistened with Cocoa Sweating |
| A very promising mycological culture medium was developed using cocoa bean shell, an industrial waste. Developed technologies for production of oyster mushroom utilizing arecanut wastes |  Oyster mushroom grown on Areca Leaf |
| Developed technologies for production of coir pith formulation of Trichoderma (Trichoderma coir pith cake) |  Trichoderma Coir Pith Cake |
| Pesticide slow release product was developed using coir pith |  Coir Pith based Pesticide slow release Product |
| PESTS Coconut Rhinoceros beetle (Oryctes rhinoceros) Metarhizium anisopliae var. major was identified as a potential pathogen on Oryctes grubs. The mass production of the fungus on solid substrates viz., cassava chips, rice bran mixture supplemented with nitrogen source and partially cooked rice media have been developed at CPCRI. The fungal spores are to be applied @ of 5 x 1011 spores / m3 on the breeding pits in which the beetles breed. The mode of infection of Oryctes Nudi virus (OrNV) on rhinoceros beetle grubs has been established. Mass production of the virus is done by rearing the grubs on virus inoculated food such as sterilized cow dung, saw dust, coir pith etc. or by mouth feeding the healthy grubs with viral suspension and rearing them on sterilized food materials. Release of 12-15 infected beetles per hectare was recommended to disseminate the virus in nature. Shade dried leaf powder of the common weed plant Clerodendron infortunatum proved its insecticidal property against Oryctes rhinoceros at 10% w/w. Incorporation of the whole plant in the breeding sites of rhinoceros beetle proved to be effective in checking the build up of the pest in the breeding sites. Application of naphthalene balls @ 10-12 g/ palm or leaf axil filling of powdered marotti cake (Hydnocarpus) @250g/palm+ fine sand 250 g or leaf axil filling with chlorantraniliprole (0.4WG) / chloridust @5g mixed with 250g of sand during April-May, and September -October proved to be effective as a prophylactic control measure for rhinoceros beetle and red weevil. A modified PVC trap was developed to be used with pheromone to attract the rhinoceros beetle adults. |
 Rhinoceros Beetle Damage with Biostages  M. anisopliae infected Grubs  Oryctes virus infected Grubs |
| Red Palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Developed IPM package for red palm weevil that includes cleaning of palm crown periodically to avoid decaying of organic debris, proper cutting, splitting and burning of red palm weevil infested palms, treating of any wounds on the palm with coal tar and stem injection with spinosad 0.013%. Prophylactic leaf axil filling with 250 g marotti oil cake (Hydnocarpus sp.) + 200 g of fine sand in leaf axils around spindle during May, September and December has been found to be effective. A red palm weevil lure ferrugineol was formulated at CPCRI. Unlike the sachets used in commercial lure the CPCRI lure was made of glass capillary of 6 cm in length and id. of 1.5 mm. Each glass capillary had 100 µl ie 78.5 mg of ferrugineol with the density of 0.76g/cc. CPCRI lure was cost effective as compared to the imported lures. The role of kairomones of red palm weevil were identified and tested under laboratory conditions. Pheromone lure when placed in isolation did not yield desirable results; hence they had to be associated with food baits. Among the various phagostimulants that were evaluated to be used in tandem with pheromone lure, it was observed that macerated plantain (200gm) or sugarcane bits attracted more weevils (an average of 8 weevils/trap/week), whilst the pheromone trap without food bait had a lowest weevil catch of 1 weevil/trap / week. Volatiles emanating from food baits are identified. Slow delivery mechanism of pheromone have been developed |
 Affected Palm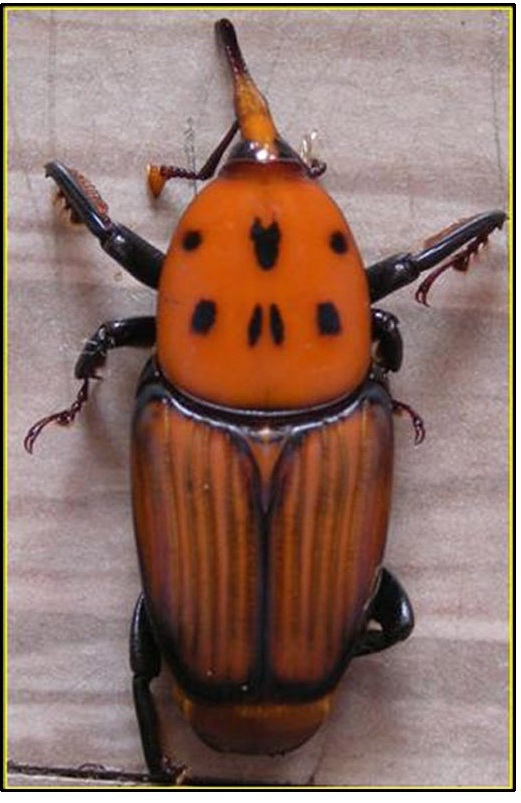  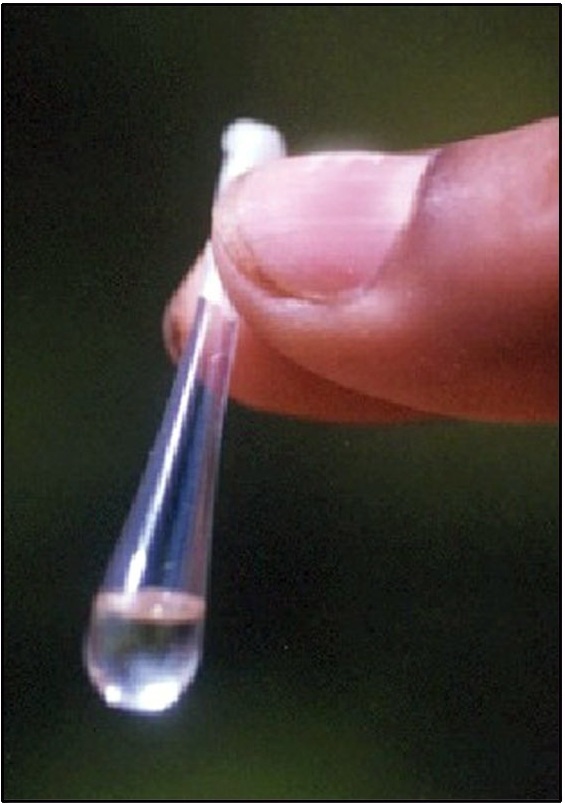 Adult (Weevil)--------Pheromone Red Palm weevil |
| Leaf eating caterpillar (Opisina arenosella) Techniques were evolved at CPCRI for mass multiplication of the promising parasitoids namely Goniozus nephantidis, Bracon brevicornis, Elasmus nephantidis and Brachymeria nosatoi which are being currently recommended for biocontrol of Opisina Release rate of the parasitoids have been fixed. G. nephantidis, E. nephantidis and B. nosatoi are to be released at fixed norms of 20.5, 49.4 and 31.9% of larval, prepupal and pupal stage of the pest respectively. In a multistage condition of the pest, a combined release of all the parasitoids @40% of each of the target pest stage is required. Mass production technique for Apanteles taragamae on early instar caterpillars of O. arenosella was evolved. Olfactory conditioning in bethylid, Goniozus nephantidis an ectoparasitoid of coconut black headed caterpillar Opisina arenosella resulted in increased host searching ability of the parasitoid released in the field. |
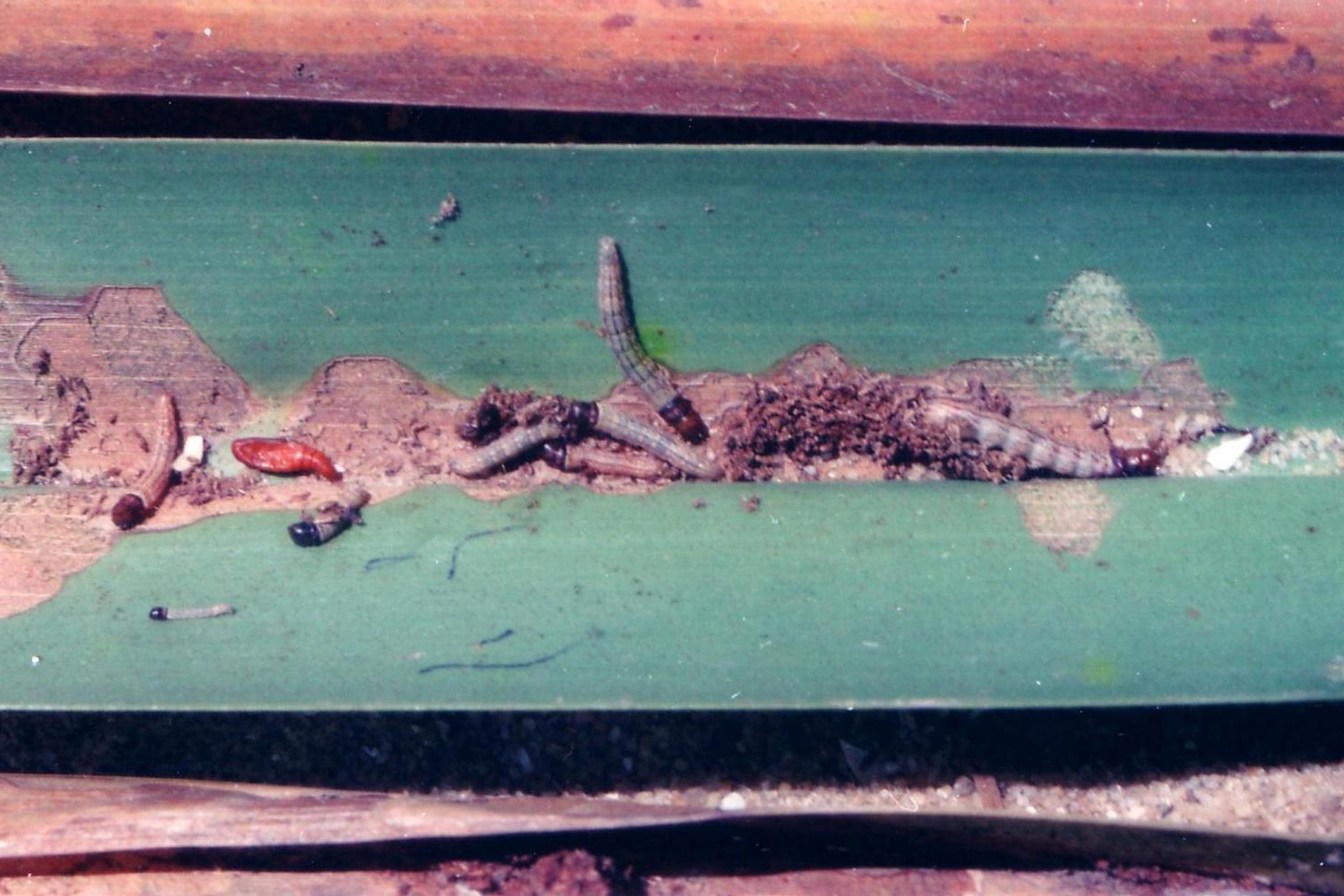 Larvae of Opisina arenosella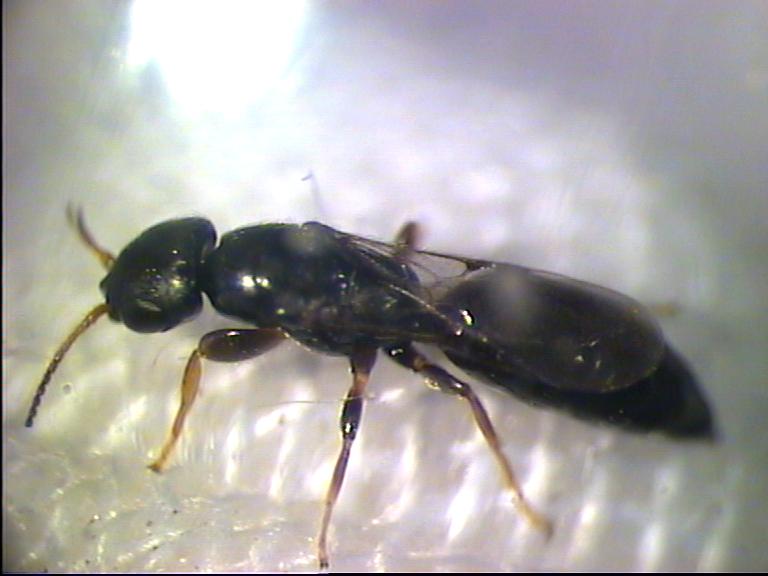  Adult of Goniozus nephantidis |
| Eriophyid mite (Aceria guerreronis) In the year 1998 CPCRI first identified and reported the occurrence of the coconut infesting eriophyid mite, Aceria guerreronis. This report was the first for the whole of Asia. Palms receiving root feeding of 10 ml Neemazal + 10 ml water and palms base drenched with 10 ml Neemazal along with soil application of Neemcake showed the highest percentage reduction in the eriophyid mite infestation. The acaropathogenic fungus Hirsutella thompsonii has been identified as potential bioagent against the eriophyid mite Aceria guerreronis. Talc based formulations of two isolates CPCRI -19 and CPCRI 51 (11) are virulent. Two rounds spraying of the fungal formulation caused a reduction to a tune of 44 – 73 %. Developed management strategies for eriophyid mite using botanochemicals. Spraying neem formulation containing 1% azadirachtin @ 4 ml/ l of water or 2% neem oil, garlic emulsion on button during April-May, Oct.-Nov. and Dec.-Jan., in such a way that all mite infested palms in an area should be covered at the shortest possible interval. | 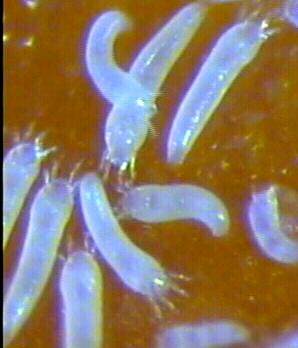 Eriophyid mite |
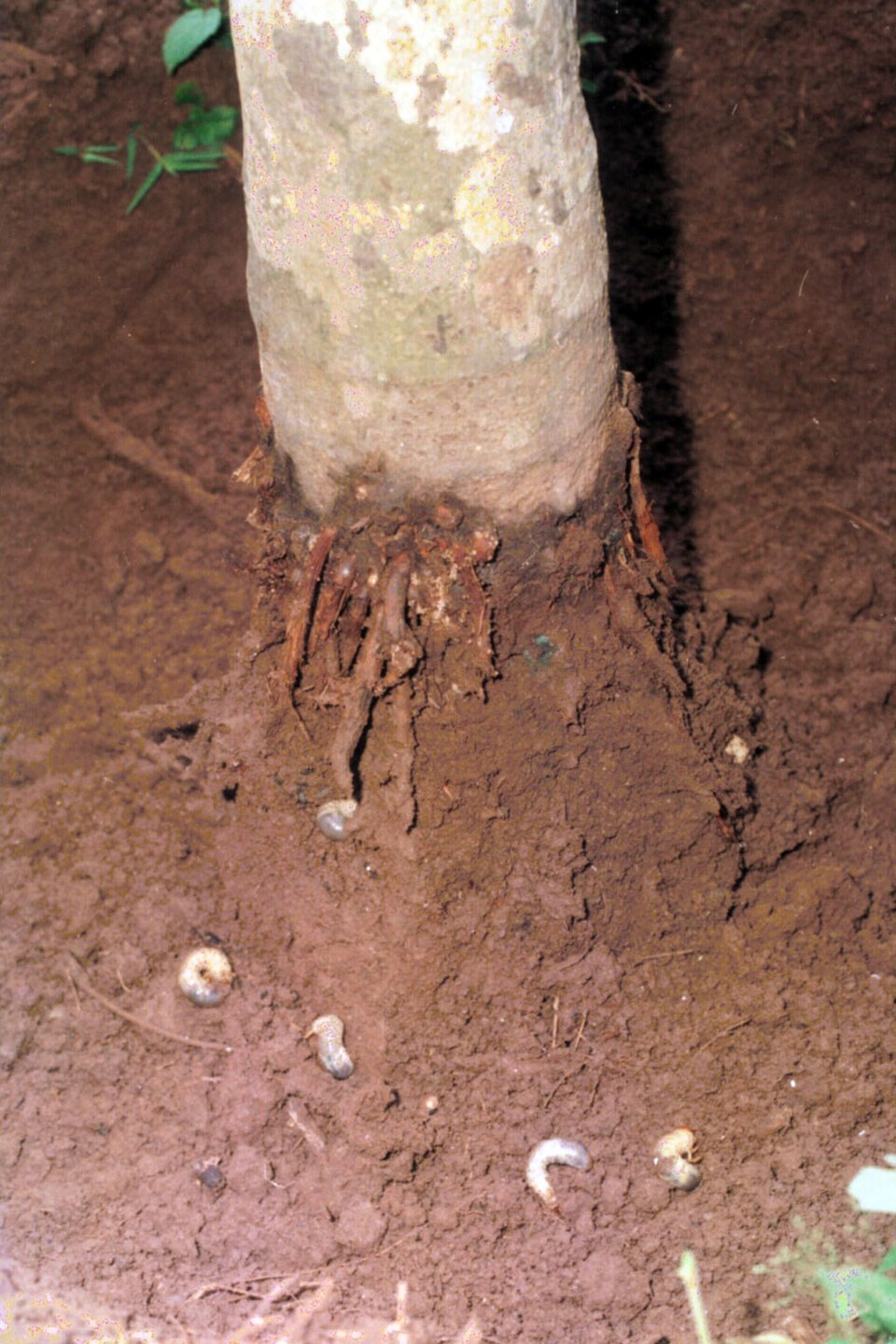
| White grub (Leucopholis coneophora) Developed IPM technology that includes deep ploughing and digging of soil during pre- and post-monsoon period, collection and destruction of adult beetles during peak emergence period in May-June. Mechanical capturing and destruction of beetles during peak emergence period. |
 Coconut root Grub |
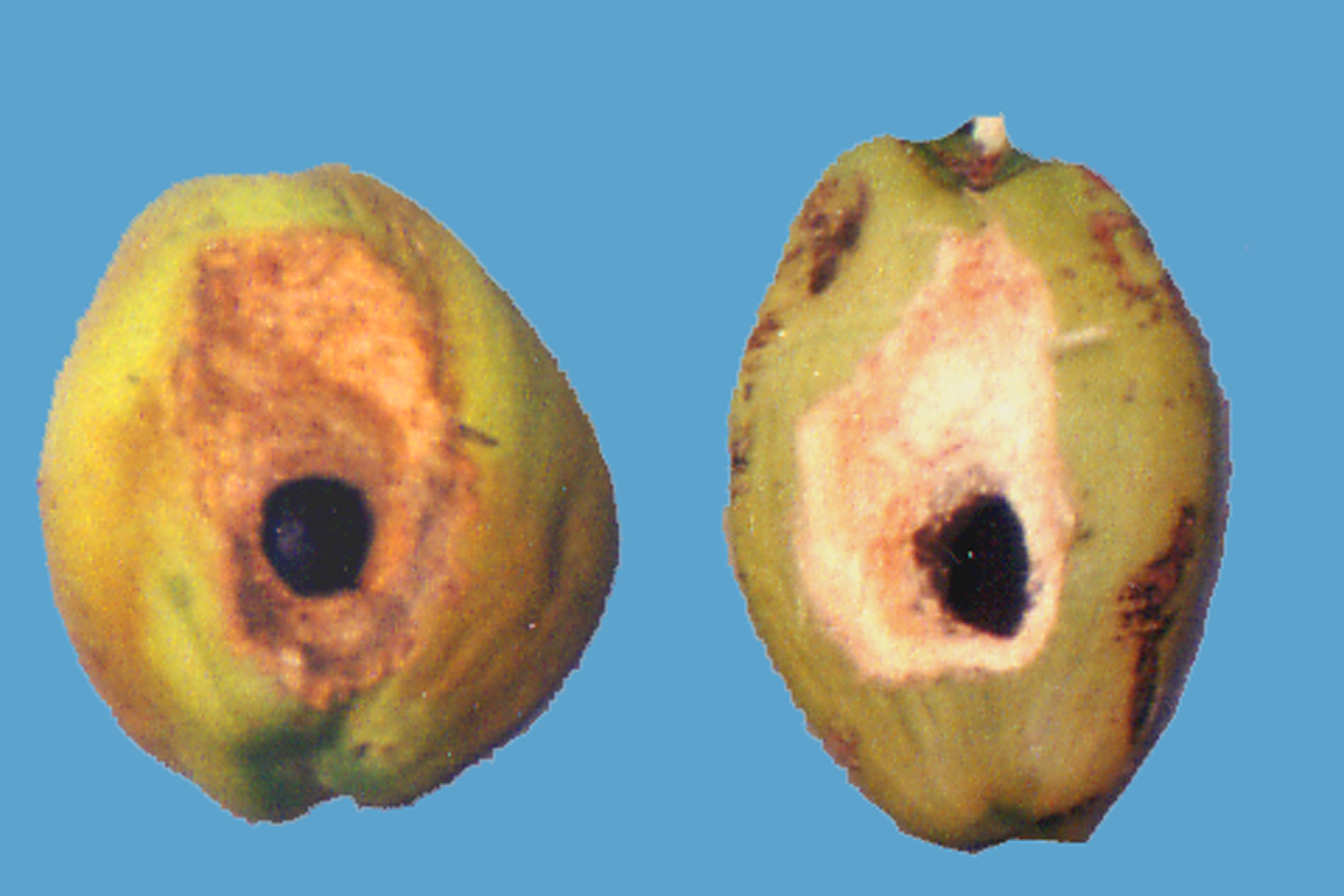
| Coreid bug (Paradasynus rostratus) Spraying of 0.5% neam oil to the button. |
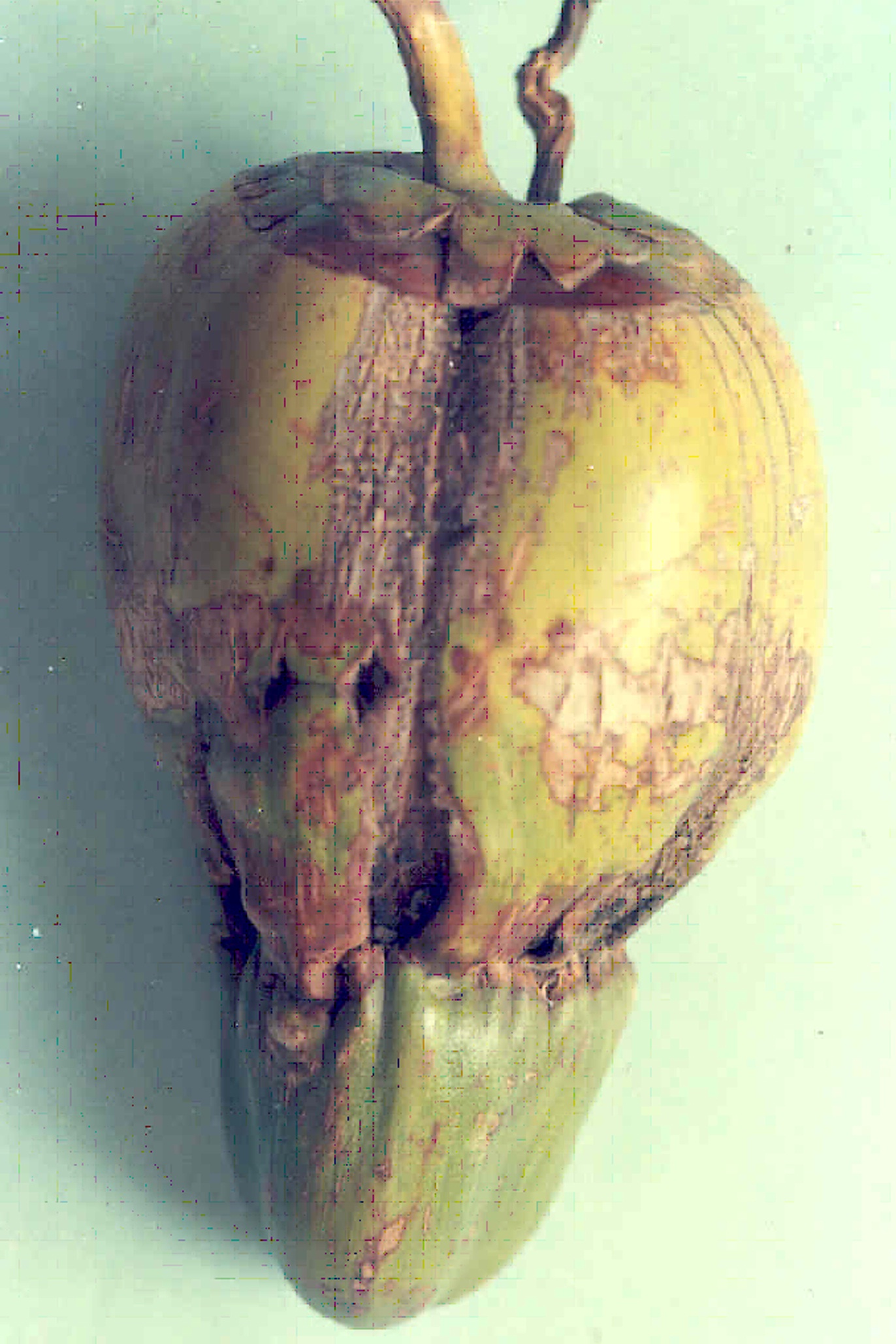 Coreid bug Damaged nut |
| Rodents(arboreal black rat Rattus rattus wroughtoni, burrowing rodents Bandicota bengalensis, B. indica, Gerbils Tatera indica) Placing of single dose anticoagulant bromodiolone (0.005%) 10 g blocks twice at an interval of 12 days on the palm crown of one tree out of every 5 trees was found effective against arboreal black rat. |
 |
| Termites (Odontotermes obesus) Drenching the nursery with 0.05 % chlorpyriphos twice at 20-25 days internal or swabbing the affected portion of the trunk in adult palms with 0.05 % chlorpyriphos solution was found effective. |
|
| Arecanut White grub (Leucopholis lepidophora Blanch) Basin application of neem cake @2kg/palm/year during June to July for re-generation of affected roots. Two round applications of insecticide is recommended viz., spraying of chlorpyriphos @ 2kg ai/ha or bifenthrin @ 2 kg ai/ha during August second week. Root zone application of chlorpyrifos 20 EC @ 7ml/palm during the last week of September. Repeating ploughing the field(5-6 times) from(Aug-Dec) to expose the grubs to predator. Mechanical capturing and destruction of beetle during peak emergence period. |
 Root Grubs of Arecanut |
| Spindle bug of arecanut (Carvalhoia arecae) Sucking of plant sap by the nymphs and adults of spindle bug result in typical linear, dark brown lesions which turn necrotic on the spindle. Damaged open leaves dry up and drop off. Severely affected spindle leaves fail to unfurl completely. Infestation in young exposed plantations results in severe manifestation of symptoms during summer months. Spray spindle leaf and inner most leaves of palms in infested plantations with dimethoate (0.06%) 30 EC 2 ml/ lit of water. |
  Spindle Bug |
| Red and White Mites (Raoiella indica and Oligonychus indicus) Spraying dimethoate (0.06%) 30EC @ 2 ml/litre of water to the lower surface of leaves was effective in reducing the pest incidence. |  Damage caused by mite |
| Immature fruit drop Feeding by Halyomorpha marmorea was identified as a cause for immature fruit drop with shrinking and browning of kernels. An egg parasitoid of the pentatomid bug, Halyomorpha marmorea which causes immature fruit drop in areca palm is identified as Anastatus bangalorensis (Hymenoptera: Eupelmidae). Spraying dimethaote (0.06%) 30EC 2ml/litre of water to the tender bunches of the affected palms and surrounding few palms. |
 Adults of Halyomorpha 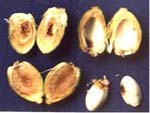 Kernal browning due to damage by Halyomorpha |
| Scale Insect Spraying dimethaote (0.06%) 30EC 2ml/litre of water to the tender bunches was found to be effective in containing scale insects. Cowpea, bhendi, bitter gourd, chillies etc, were identified as alternate host for this pest. Ladybird beetle,Chilocorus nigrita was identified as an effective predator against the scale insects. |
 Arecanut infested by Scales Arecanut infested by Scales |
| Cocoa Tea mosquito bug The damage symptoms like necrosis and dieback of shoots, bark roughening, destruction of flowers and cherelles were identified as symptoms due to damage. In cherelles, feeding punctures cause distortion during growth. Yield reduction was reported up to 30 to 40 %. |
 Adults of tea musquito Bug  Damage caused by Feeding |
| Rodents Placing 10g Bromodiolone (0.005%) wax cakes on the branches of cocoa trees twice at an interval of 10-12 days will check the rat damage was found as an effective technique to manage the rodents |
 |
| Squirrels Squirrels gnaw the pods in the center and damage only the mature ones. They feed on the mucilage covering of the beans. Trapping with wooden or wire mesh single catch ‘live’ trap with ripe coconut kernel as the bait is effective. Timely harvest of the pods will help in increasing the efficiency of poison baiting as well as trapping. |
 |