Genetics and Plant Breeding
- World's largest germplasm collection of coconut (comprising 401accessions 269 indigenous and 132 exotic) is being maintained in the Institute. The exotic collections are from 28 countries of South Asia, South-East Asia, Africa, Caribbean Islands, Indian Ocean Islands and Pacific Ocean Islands.
- Designated as National Active Germplasm Site for Plantation crops and host for National Gene Banks for coconut, arecanut and cocoa.
- Host to International Coconut Gene Bank for South Asia under Coconut Genetic Resources Network of Bioversity
- Released twelve improved varieties of coconut (Chandra Kalpa, Kera Chandra, Chowghat Orange Dwarf, Kalpa Pratibha, Kalpa Dhenu, Kalpa Mitra, Kalparaksha, Kalpasree, Kalpatharu, Kalpa Jyothi, Kalpa Surya and Kalpa Haritha) .
|
 |
- Released five high yielding hybrids of coconut - Chandra Sankara, Kera Sankara, Chandra Laksha, Kalpa Samrudhi and Kalpa Sankara.
- Dwarf varieties viz., Chowghat Orange Dwarf, Kalpa Jyothi, Kalpa Surya were released exclusively for tender coconut
- Kalpa Pratibha, Kalpa Haritha, Kalpa Samrudhi, Chgandra Sankara, Kalparaksha and Kalpasree were released as dual purpose varieties suitable for copra and tender nuts
- Chandra Kalpa, Kalpa Mitra, Kalpa Dhenu, Kalpa Pratibha Kalpatharu and Kalpa Samrudhi are relatively tolerant to drought.
- Kalpa Haritha is comparatively free from Eriophyid mite infestation amidst heavely infested palms of other varieties
- Dwarf varieties viz., Kalparaksha and Kalpasree are recommended for root (wilt) affected areas with higher degree of root (wilt) disease resiatnce.
- The hybrid Kalpa Sankarais released for root (wilt) disease tracts for its tolerance to the disease
- Kalpatharu is released for ball copra production
- Coconut descriptors prepared for 74 accessions and important accessions registered.
|
 |
- In arecanut,164 germplasm collections of which 23 exotic and 141 indigenous are conserved at CPCRI,RS, Vittal
- Released six high yielding varieties (Mangala, Sumangala, Sreemangala, Mohitnagar, Swarnamangala and Kahikuchi) and two hybrids of arecanut (VTLAH1 and VTLAH2)
|
 |
- In cocoa, 321 germplasm collections including 281 exotic and 40 indigenous clones are being conserved under Arecanut and Coconut at CPCRI, Regional Station, Vittal, Karnataka.
- Seven varieties of cocoa are released including four hybrids (VTLCH-1, VTLCH-2, VTLCH-3 and VTLCH-4), one clone VTLCC-1 and two selections VTLCS-1 and VTLCS-2. They exhibited high pod and dry bean yields, bigger and bold beans with less shell contents, high nib recovery, richness in fat, tolerance to water stress and suitability to be grown both in arecanut and coconut gardens.
- Softwood grafting technology has been standardized in cocoa and utilised for mass multiplication.
- Scion bank and compact block on varieties are established with mother trees.
- Six bi-clonal and one poly-clonal orchards are established with 1100 trees for F1 seed production at CPCRI, Research Centre, Kidu, Karnataka.
- Quality planting material of mandate crops are being produced to the extent of more than 1.2 lakh coconut seed nuts, 3 lakh arecanut seed nuts and 1.1 lakh cocoa grafts/ seedlings/ seed pods.
- CPCRI nurseries at Kasaragod, Kidu and Vittal are recognized and accredited under 4* category by National Horticulture Board.
|
 |
Biotechnology
- Protocol for regeneration of coconut plantlets from plumule explants through somatic embryogenesis developed.
- Cryopreservation techniques have been standardized for mature coconut zygotic embryos and coconut pollen
|
 |
- DNA finger printing using molecular markersviz. RAPD, AFLP, DAF and microsatellites have been carried out in coconut and cocoa accessions to document the genetic integrity and diversity. About 139 coconut accessions have been characterized using SSR markers. Mother palms used for seed production have been genotyped to develop markers for hybridity. Diverse germplasm accessions including dwarfs and talls are being used for developing markers for dwarf plant habit.
- Tissue culture protocol has been standardised for mass multiplication of arecanut from inflorescence explants and genetic fidelity ofin vitro derived plantlets has been assesed using molecular markers
|
  |
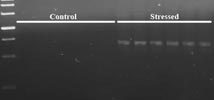
- Transcripts induced during water stress have been identified using differential display RT-PCR technique (DDRT-PCR). The clones were characterized into different functional groups based on the sequence similarities.
Cloning and identification of transcripts induce during water-stress in coconut
- The nucleotide and protein sequences pertaining to known genes induced during water stressviz.DREB, 14-3-3, aquaporins,9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase,WRKY ,NAC and epicuticular wax (CER, GL and Wax) were retrieved from the NCBI. Nucleotide sequences coding for conserved domain amino acids were selected for oligomer designing. The degenerate primers were used to amplify putative water stress responsive genes in coconut via RT-PCR. Amplicons of expected sizes were eluted, cloned and sequenced. Positive sequences were deposited in Genbank.
|
 |
Isolation of genes induced during somatic embryogenesis in coconut.
- The nucleotide and protein sequences pertaining to genes induced during somatic embryogenesisviz. SERK (somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase) and BBM (BABY BOOM) were retrieved from the NCBI. Nucleotide sequences coding conserved domain amino acid was selected for oligomer designing. These degenerate primers were used to amplify, clone and sequenceSERK andBBM genes in coconut
Cross transferability of SSR makers from coconut to related palms.
- To study the cross transferability of SSR markers from coconut in other palms, 86 microsatellite markers specific to coconut were screened out of which 55 primers gave span, clear bands of expected size range (100-300bp). These primers were tested for their cross-taxa amplification in oil palm, arecanut, palmyrah and date palm. The percentage of cross-amplification of coconut SSR loci in other palms were 36.36% in oil palm, 29.09% in arecanut, 18.18% in palmyrah and 12.70% in date palm.
|
 |
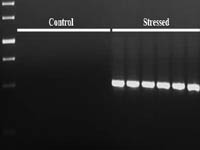
Cloning of MAP kinase induced during water stress in coconut.
- Coconut plantletsin vitro were subjected to water stress with PEG treatment and RNA was isolated from the leaves. Degenerate primers, designed for amplification ofMAP kinase, were used in single-step RT-PCR reactions with the isolated RNA as template. Bands of expected size were eluted, cloned and sequenced. One fragment showed homology to knownMAP kinase from other plants.
Bioinformatics
- Under the Bioinformatics initiative, several comprehensive databases for the mandate crops have been developed.
|
 |











